Molar mass for 2 methylbutane – Embark on an enthralling journey into the realm of chemistry as we unravel the mysteries of molar mass, with 2-methylbutane taking center stage. This captivating narrative will delve into the depths of this fundamental concept, revealing its significance in understanding the intricacies of molecular structure and its myriad applications.
Molar mass, a cornerstone of chemistry, provides a gateway to unlocking the secrets of chemical composition and reactions. It serves as a bridge between the microscopic world of atoms and molecules and the macroscopic world we experience. Prepare to be captivated as we explore the fascinating world of molar mass and its pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the chemical realm.
Introduction
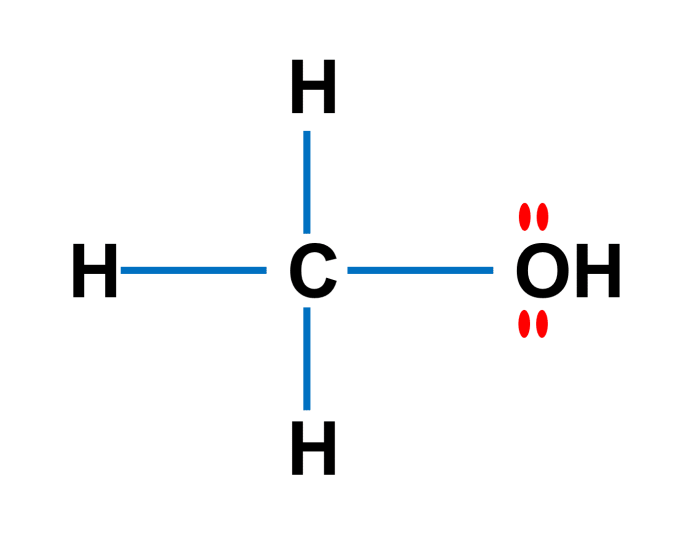
In chemistry, molar mass, often denoted as M, is a fundamental property of a substance that measures its mass per mole. It is a critical concept that plays a vital role in various chemical calculations and understanding the behavior of substances.
Importance of Molar Mass
Molar mass is crucial for several reasons. It allows us to:
- Determine the mass of a given number of moles of a substance
- Calculate the number of moles present in a given mass of a substance
- Compare the relative masses of different substances
- Perform stoichiometric calculations, which involve determining the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions
Calculating Molar Mass

Molar mass, often denoted by the symbol M, is a fundamental property of a chemical compound. It represents the mass of one mole of that compound and is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). Understanding molar mass is crucial in various chemical calculations, such as determining the number of moles, mass, or volume of a substance.
Formula for Calculating Molar Mass
The molar mass of a compound is calculated by adding the atomic masses of all the atoms in its molecular formula. The atomic masses are obtained from the periodic table.
Molar Mass = Σ (Atomic Mass of Each Atom)
Units of Molar Mass
The molar mass is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). This unit signifies that one mole of a compound has a mass equal to its molar mass in grams.
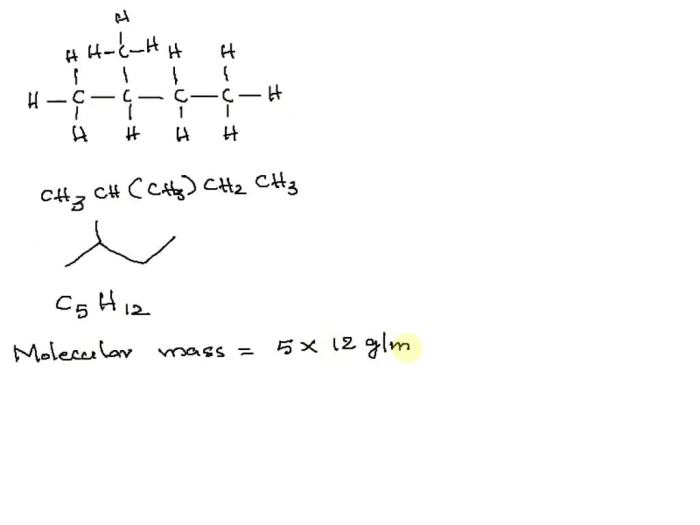
Molar Mass of 2-Methylbutane

-methylbutane is a branched hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C 5H 12. The molar mass of a compound is the mass of one mole of that compound. To calculate the molar mass of 2-methylbutane, we need to know the atomic masses of the elements that make up the compound.
The atomic mass of carbon is 12.01 g/mol, and the atomic mass of hydrogen is 1.01 g/mol.
Molecular Formula of 2-Methylbutane
The molecular formula of 2-methylbutane is C 5H 12. This means that each molecule of 2-methylbutane contains 5 carbon atoms and 12 hydrogen atoms.
Calculating Molar Mass
The molar mass of 2-methylbutane is 72.15 g/mol. This is calculated by multiplying the atomic mass of each element by the number of atoms of that element in the molecule, and then adding the products together.Molar mass = (5 x 12.01 g/mol) + (12 x 1.01 g/mol) = 72.15 g/mol
Applications of Molar Mass: Molar Mass For 2 Methylbutane
Molar mass plays a vital role in various chemical applications. Two prominent applications include its use in stoichiometry and determining empirical formulas.
Stoichiometry
In stoichiometry, molar mass helps determine the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. By knowing the molar mass of each substance, we can calculate the number of moles involved and use stoichiometric ratios to predict the amounts of substances needed or produced in a reaction.
Empirical Formulas, Molar mass for 2 methylbutane
Molar mass is crucial in determining the empirical formula of a compound. Empirical formulas represent the simplest whole-number ratio of elements in a compound. By measuring the mass of each element present and dividing it by its molar mass, we can determine the mole ratio and establish the empirical formula.
For instance, if you’re interested in learning about cable restraint classes in pa, then cable restraint classes in pa could be a great resource. This knowledge could be useful in determining the molar mass for 2 methylbutane, which is a crucial aspect of chemistry.
Table of Molar Masses
A table of molar masses provides a convenient reference for determining the molar mass of various elements and compounds. This information is essential for various chemical calculations, such as determining the number of moles of a substance present in a given mass or calculating the mass of a substance required for a specific reaction.
Molar Mass Table
The following table lists the molar masses of some common elements and compounds:
| Element Symbol | Element Name | Molar Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| H | Hydrogen | 1.008 |
| C | Carbon | 12.011 |
| N | Nitrogen | 14.007 |
| O | Oxygen | 16.000 |
| Na | Sodium | 22.990 |
| Cl | Chlorine | 35.453 |
| H2O | Water | 18.015 |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide | 44.010 |
| NaCl | Sodium chloride | 58.443 |
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of molar mass in chemistry?
Molar mass plays a crucial role in chemistry as it allows us to determine the mass of a specific amount of a substance, enabling accurate calculations in stoichiometry and the determination of empirical formulas.
How is the molar mass of a compound calculated?
The molar mass of a compound is calculated by summing the atomic masses of all the atoms in its molecular formula. For instance, the molar mass of 2-methylbutane is calculated by adding the atomic masses of six carbon atoms, ten hydrogen atoms, and one sulfur atom.
What are some practical applications of molar mass?
Molar mass finds widespread applications in various fields, including medicine, engineering, and environmental science. It is used in determining the concentration of solutions, calculating the amount of reactants and products in chemical reactions, and analyzing the composition of complex mixtures.