Art-labeling activity parts of the thoracic cage – Embark on an artistic exploration of human anatomy with our captivating art-labeling activity. Dive into the intricacies of the thoracic cage, unraveling its structure and significance through an interactive and engaging learning experience.
This activity invites you to delve into the anatomy of the thoracic cage, examining each bone’s location, function, and interconnections. Prepare to enhance your understanding of this vital skeletal framework, essential for respiration and protection.
Thoracic Cage Anatomy
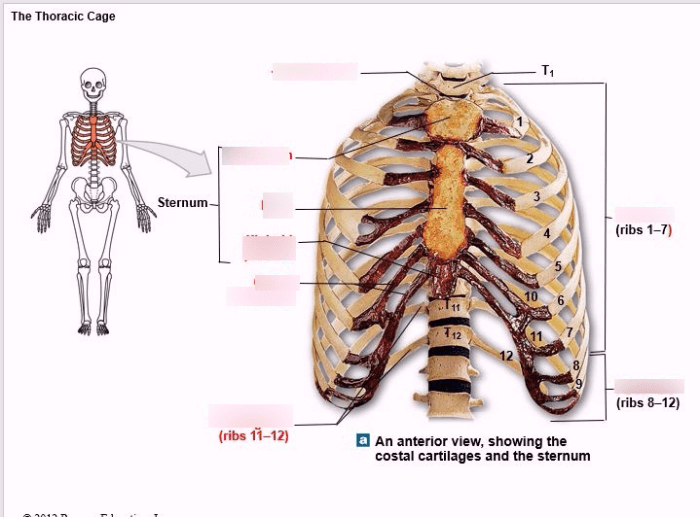
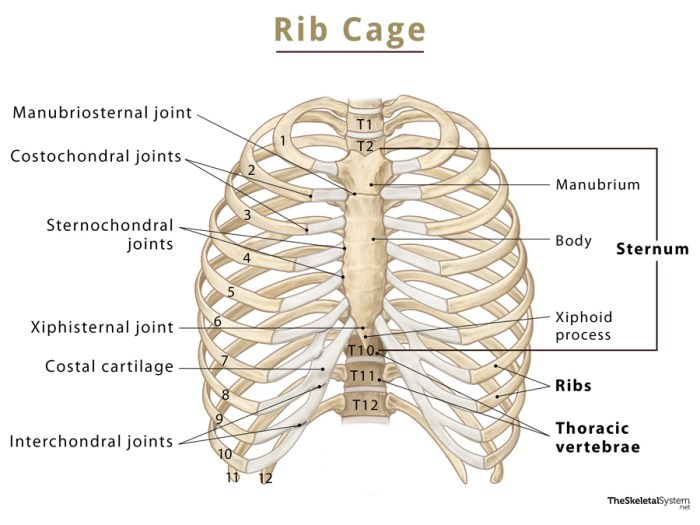
The thoracic cage, also known as the rib cage, is a complex structure that forms the protective framework for the vital organs of the chest cavity. It consists of 12 pairs of ribs, 12 thoracic vertebrae, and the sternum.The ribs are long, curved bones that extend from the thoracic vertebrae to the sternum.
They are connected to the vertebrae by the costovertebral joints and to the sternum by the costosternal joints. The ribs form the lateral and anterior walls of the thoracic cage.The thoracic vertebrae are the 12 vertebrae that make up the thoracic spine.
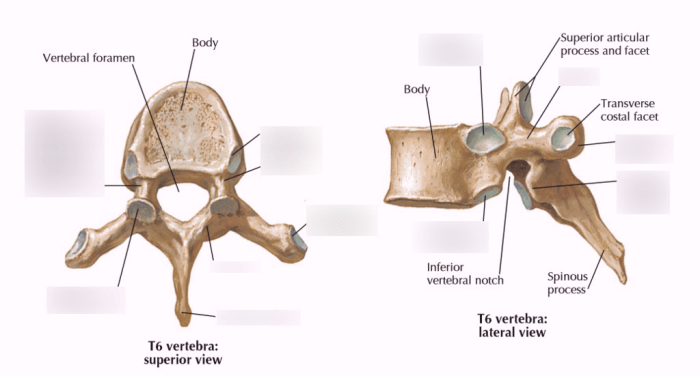
They are located between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. The thoracic vertebrae are connected to each other by the intervertebral discs and the facet joints.The sternum is a flat, triangular bone that forms the anterior wall of the thoracic cage.
It is located in the midline of the chest and is connected to the ribs by the costosternal joints.
Art-Labeling Activity, Art-labeling activity parts of the thoracic cage
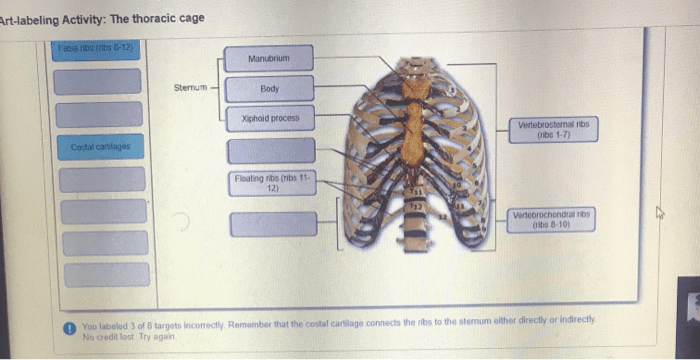
An art-labeling activity is a valuable tool for teaching about the parts of the thoracic cage. This activity allows students to visualize the anatomy of the thoracic cage and to learn the names and functions of the different bones.To create an art-labeling activity, you will need a diagram of the thoracic cage.
You can find a diagram online or in a textbook. Once you have a diagram, you can create a table with four columns: bone name, location, function, and image.Fill out the table with information about each bone of the thoracic cage.
Be sure to include the following information:* Bone name: The name of the bone.
Location
The location of the bone in the thoracic cage.
Function
The function of the bone.
Image
A picture of the bone.
Labeling Methods
There are different methods for labeling the parts of the thoracic cage in an art-labeling activity. You can use arrows, lines, or text boxes to label the bones.*
-*Arrows
Arrows can be used to point to the bones and to label them. This is a simple and effective way to label the bones, but it can be difficult to draw arrows that are clear and concise.
-
-*Lines
Lines can be used to connect the bones to their labels. This is a more complex way to label the bones, but it can be more clear and concise than using arrows.
-*Text boxes
Text boxes can be used to place the labels next to the bones. This is a simple and effective way to label the bones, but it can take up more space than using arrows or lines.
Educational Benefits
Using an art-labeling activity to teach about the thoracic cage has several educational benefits. This activity can help students to:* Visualize the anatomy of the thoracic cage.
- Learn the names and functions of the different bones.
- Understand the relationships between the different bones.
- Apply their knowledge of the thoracic cage to other areas of study, such as physiology and pathology.
Query Resolution: Art-labeling Activity Parts Of The Thoracic Cage
What is the purpose of the thoracic cage?
The thoracic cage provides structural support, protects vital organs, and facilitates respiration by allowing for lung expansion.
How many bones form the thoracic cage?
The thoracic cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs, 12 thoracic vertebrae, and the sternum.
What is the function of the sternum?
The sternum, also known as the breastbone, connects the ribs and provides attachment points for muscles involved in respiration.