Chapter 9 right triangles and trigonometry – Chapter 9: Right Triangles and Trigonometry introduces students to the fascinating world of trigonometry, where the relationship between angles and sides of right triangles takes center stage. This chapter provides a comprehensive exploration of the Pythagorean Theorem, trigonometric ratios, special right triangles, and their diverse applications in real-world scenarios.
The Pythagorean Theorem serves as the foundation for understanding right triangles, enabling us to calculate unknown side lengths using the relationship between the square of the hypotenuse and the squares of the other two sides. Trigonometric ratios, such as sine, cosine, and tangent, provide a powerful tool for analyzing angles and distances in right triangles, unlocking a wide range of applications in fields like navigation, surveying, and architecture.
Pythagorean Theorem
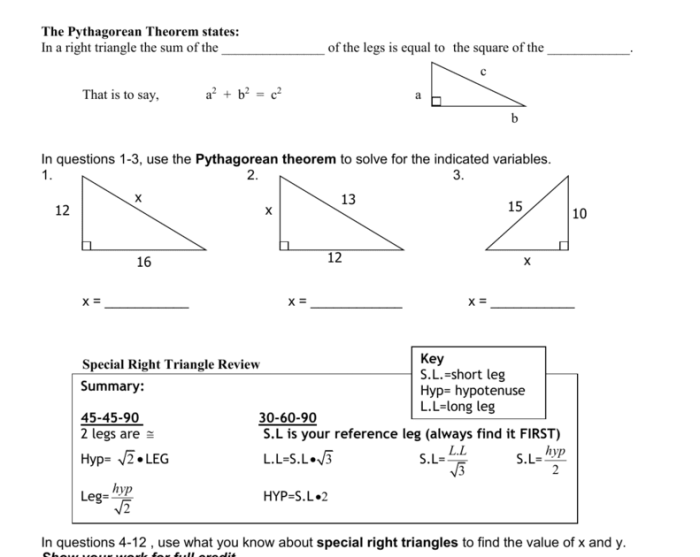
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental theorem in geometry that states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
a2+ b 2= c 2
where a and b are the lengths of the two legs of the right triangle, and c is the length of the hypotenuse.
The Pythagorean Theorem has numerous applications in solving problems involving right triangles, such as finding the length of a side, determining the height of an object, or calculating the distance between two points.
Examples of Pythagorean Theorem Applications, Chapter 9 right triangles and trigonometry
- Finding the length of the hypotenuse: If the lengths of the legs of a right triangle are 3 and 4, then the length of the hypotenuse can be found using the Pythagorean Theorem:
- a 2+ b 2= c 2
- 3 2+ 4 2= c 2
- 9 + 16 = c 2
- c 2= 25
- c = √25 = 5
- Determining the height of an object: Suppose you have a ladder that is 10 feet long and is leaning against a wall. The bottom of the ladder is 6 feet from the wall. Using the Pythagorean Theorem, you can find the height of the ladder where it touches the wall:
- a 2+ b 2= c 2
- 6 2+ 8 2= c 2
- 36 + 64 = c 2
- c 2= 100
- c = √100 = 10
Trigonometric Ratios
Trigonometric ratios are functions that relate the lengths of the sides of a right triangle to the angles of the triangle.
The three main trigonometric ratios are:
- Sine (sin): The ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse
- Cosine (cos): The ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse
- Tangent (tan): The ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side
These ratios can be calculated using the following formulas:
sin θ = opposite / hypotenuse
cos θ = adjacent / hypotenuse
tan θ = opposite / adjacent
Trigonometric ratios are used extensively in solving problems involving angles and distances in right triangles.
Examples of Trigonometric Ratio Applications
- Finding the height of an object: Suppose you have a flagpole that casts a shadow that is 10 feet long. The angle of elevation from the end of the shadow to the top of the flagpole is 30 degrees.
Using the tangent function, you can find the height of the flagpole:
- tan θ = opposite / adjacent
- tan 30° = height / 10
- height = 10 – tan 30°
- height ≈ 5.77 feet
- Determining the distance to an object: Suppose you are standing on a cliff that is 100 feet high. You see a boat in the distance, and the angle of depression from your eyes to the boat is 15 degrees. Using the sine function, you can find the distance from the cliff to the boat:
- sin θ = opposite / hypotenuse
- sin 15° = 100 / distance
- distance = 100 / sin 15°
- distance ≈ 386.4 feet
Question & Answer Hub: Chapter 9 Right Triangles And Trigonometry
What is the Pythagorean Theorem?
The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
What are trigonometric ratios?
Trigonometric ratios are ratios of the lengths of sides in a right triangle that involve an angle and its opposite, adjacent, or hypotenuse sides.
What are special right triangles?
Special right triangles are right triangles with specific angle measures, such as the 45-45-90 triangle, the 30-60-90 triangle, and the 60-30-90 triangle, which have unique properties and relationships between their side lengths.