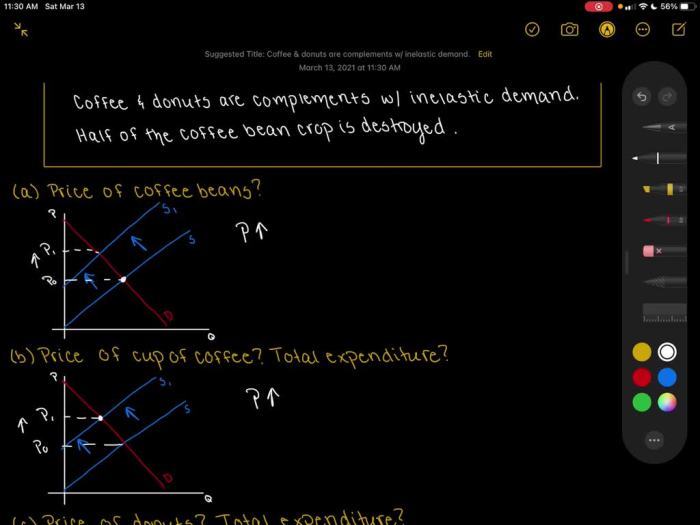
Cups of coffee and donuts are complements, meaning they are goods that are often consumed together. This pairing has become a staple in many cultures, with coffee shops and donut shops often being found in close proximity. The complementary relationship between coffee and donuts has a significant impact on their demand, supply, pricing, and marketing strategies.
The demand for coffee and donuts is interdependent. When the price of coffee increases, the demand for donuts decreases, and vice versa. This is because consumers often view coffee and donuts as a single product, and a change in the price of one good will affect the demand for the other.
Additionally, the complementary relationship between coffee and donuts creates opportunities for cross-selling and upselling, as customers who purchase one item are more likely to purchase the other.
Complementary Goods
Complementary goods are those that are used together and increase the satisfaction of consumers when consumed jointly. They exhibit the following characteristics:
- Positive cross-price elasticity of demand: When the price of one good decreases, the demand for the other good increases.
- Negative cross-price elasticity of supply: When the price of one good increases, the supply of the other good decreases.
Cups of coffee and donuts exhibit complementary characteristics. When the price of coffee decreases, the demand for donuts increases, and vice versa. This is because consumers enjoy consuming coffee and donuts together.
Demand and Supply

Complementary goods affect demand and supply in the following ways:
- Increased demand: When the price of one complementary good decreases, the demand for both goods increases.
- Increased supply: When the price of one complementary good increases, the supply of both goods decreases.
For example, if the price of coffee decreases, the demand for both coffee and donuts will increase. This is because consumers will substitute coffee for other beverages and purchase more donuts to complement their coffee consumption.
Pricing Strategies: Cups Of Coffee And Donuts Are Complements
Businesses can optimize pricing for complementary goods to maximize profits by employing the following strategies:
- Bundling: Offering complementary goods together at a discounted price.
- Price discrimination: Charging different prices for complementary goods to different customer segments.
- Loyalty programs: Rewarding customers for purchasing complementary goods together.
For example, a coffee shop could offer a bundle that includes a cup of coffee and a donut at a discounted price. This would encourage customers to purchase both items together and increase the shop’s profits.
Marketing and Promotion
Marketing and promotional strategies for complementary goods focus on:
- Promoting the joint consumption of goods.
- Highlighting the complementary nature of the goods.
- Creating a positive brand image for both goods.
For example, a coffee shop could run a marketing campaign that emphasizes the perfect pairing of coffee and donuts. This could include creating social media posts, running print advertisements, and offering in-store promotions.
Cross-Selling and Upselling
Cross-selling and upselling are techniques used to increase sales of complementary goods:
- Cross-selling: Suggesting complementary goods to customers who are already purchasing one of the goods.
- Upselling: Encouraging customers to purchase a more expensive or premium version of the complementary good.
For example, a coffee shop could cross-sell donuts to customers who are ordering coffee. They could also upsell a specialty coffee drink to customers who are purchasing a regular cup of coffee.
Customer Perception

Customer perception influences the demand for complementary goods. Factors that affect customer preferences include:
- Personal tastes and preferences.
- Social and cultural norms.
- Marketing and advertising.
For example, in some cultures, coffee and donuts are seen as a traditional breakfast pairing. This perception can influence customers’ demand for both goods.
Question Bank
What are complementary goods?
Complementary goods are goods that are often consumed together. When the price of one good increases, the demand for the other good decreases, and vice versa.
How are coffee and donuts complementary goods?
Coffee and donuts are complementary goods because they are often consumed together. The demand for coffee increases when the price of donuts decreases, and vice versa.
What are some pricing strategies for complementary goods?
Pricing strategies for complementary goods include bundling, cross-selling, and upselling. Bundling involves selling two or more goods together for a single price. Cross-selling involves promoting one good to customers who have purchased another good. Upselling involves offering a more expensive version of a good to customers who have purchased a less expensive version.