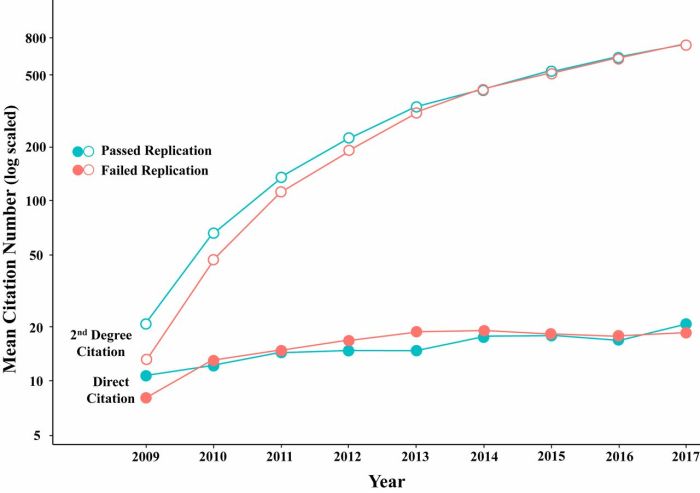
Failures to replicate findings share the same problems as has become a prevalent issue in scientific research, casting doubt on the reliability of published results. This article delves into the common methodological flaws that contribute to replication failures, explores the implications for scientific integrity, and discusses potential solutions to address this crisis.
The replication crisis has raised concerns about the trustworthiness of scientific findings, with high-profile studies failing to replicate. Understanding the underlying problems is crucial for restoring confidence in research and ensuring the advancement of knowledge.
Replication Crisis in Science

The replication crisis in science refers to the widespread failure of scientific studies to replicate, or reproduce, the results of previous studies. This has raised concerns about the reliability and trustworthiness of scientific findings.
Some high-profile examples of studies that failed to replicate include the 2011 study that claimed to have found a link between the MMR vaccine and autism, and the 2015 study that claimed to have found a way to edit genes in human embryos.
The replication crisis has implications for the reliability of scientific findings. It means that many scientific claims may not be as well-supported as we thought, and that some of the conclusions we have drawn from scientific research may be incorrect.
Common Problems in Replication Failures
There are a number of methodological flaws that can contribute to replication failures. These include:
- Small sample sizes:Studies with small sample sizes are more likely to produce false positive results, which are results that appear to be statistically significant but are actually due to chance.
- Poor experimental design:Studies that are not well-designed are more likely to produce biased results. For example, studies that do not use a control group or that do not randomize participants are more likely to produce biased results.
- Data analysis errors:Errors in data analysis can also lead to replication failures. For example, using the wrong statistical test or making mistakes in data entry can lead to incorrect conclusions.
Addressing Replication Failures
There are a number of steps that researchers can take to address the replication crisis. These include:
- Using larger sample sizes:Studies with larger sample sizes are less likely to produce false positive results.
- Improving experimental design:Studies that are well-designed are more likely to produce unbiased results. For example, studies that use a control group and that randomize participants are more likely to produce unbiased results.
- Reducing data analysis errors:Researchers can reduce data analysis errors by using the correct statistical tests and by carefully checking their data for errors.
- Making data and analysis code publicly available:This allows other researchers to replicate the study and to check for errors.
- Collaborating with other researchers:Collaboration can help to improve the quality of research and to reduce the risk of replication failures.
Future of Replication in Science, Failures to replicate findings share the same problems as
The replication crisis is a serious challenge for science. However, it is also an opportunity to improve the quality of scientific research. By addressing the problems that contribute to replication failures, we can make science more reliable and trustworthy.
Some potential solutions to the replication crisis include:
- Meta-analyses:Meta-analyses are studies that combine the results of multiple studies. They can provide more reliable results than individual studies.
- Pre-registration:Pre-registration is the process of registering a study before it is conducted. This helps to prevent researchers from changing the study design or data analysis plan after the data has been collected.
- Open access publishing:Open access publishing makes research findings freely available to everyone. This allows other researchers to replicate the study and to check for errors.
Expert Answers: Failures To Replicate Findings Share The Same Problems As
What are the most common problems that contribute to replication failures?
Common problems include small sample sizes, inadequate control groups, publication bias, and researcher bias.
How can researchers address the replication crisis?
Researchers can adopt rigorous experimental designs, preregister studies, share data openly, and collaborate with other researchers.
What are the ethical implications of failing to replicate findings?
Failing to replicate findings can undermine trust in science, lead to wasted resources, and hinder scientific progress.