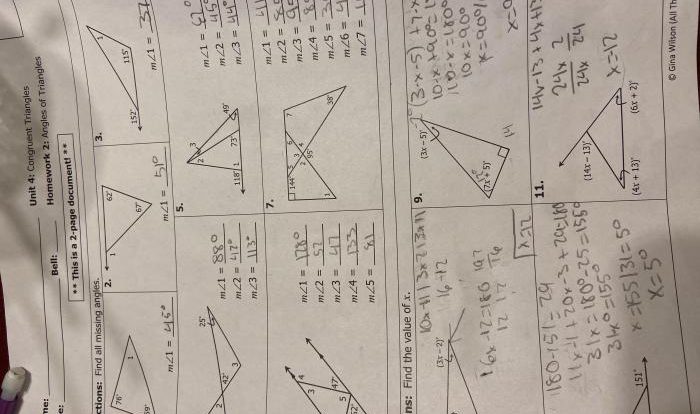
Geometry Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof Answer Key: Unlocking Mathematical Truths: Delve into the captivating world of geometry, where reasoning and proof are the cornerstones of mathematical discovery. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of geometric reasoning and proof, empowering you to solve complex problems and unravel the mysteries of shapes and spaces.
From the fundamental concepts of reasoning and proof to the diverse types of reasoning and methods of proof employed in geometry, this guide provides a thorough exploration of the subject. With clear explanations, engaging examples, and a comprehensive answer key, you’ll gain a deep understanding of the principles that govern geometric thinking.
Geometry Chapter 2: Reasoning and Proof
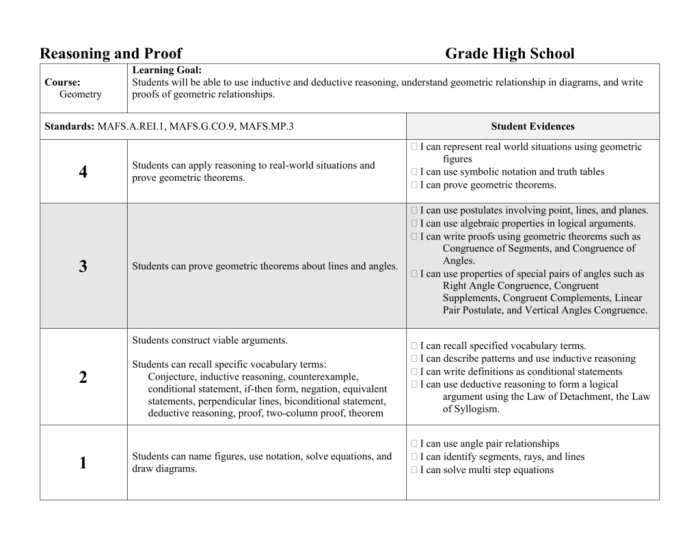
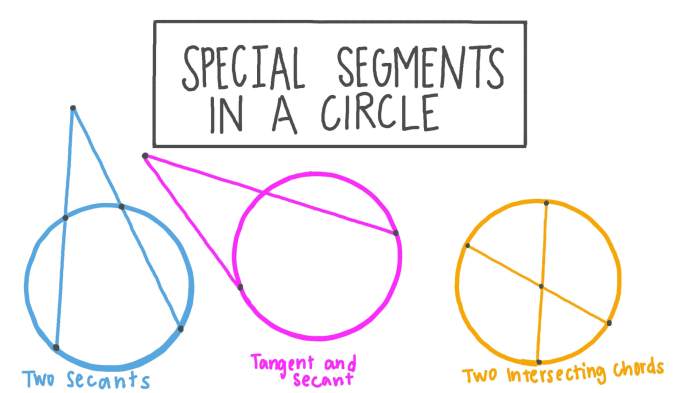
Geometry Chapter 2 introduces the fundamental concepts of reasoning and proof in geometry. Reasoning involves using logic and evidence to draw conclusions, while proof is a rigorous argument that demonstrates the validity of a statement.
Types of Reasoning in Geometry
Deductive Reasoning
Deductive reasoning involves drawing conclusions from a set of given premises. If the premises are true, then the conclusion must also be true.
Example: If all squares are rectangles, and all rectangles have four sides, then all squares have four sides.
Inductive Reasoning
Inductive reasoning involves making generalizations based on patterns or observations. While inductive reasoning can provide strong evidence, it does not guarantee that the conclusion is true.
Example: I have observed that every time I flip a coin, it lands on heads. Therefore, I conclude that all coin flips will land on heads.
Geometric Reasoning, Geometry chapter 2 reasoning and proof answer key
Geometric reasoning involves using geometric properties and relationships to draw conclusions about geometric figures.
Example: If two lines are parallel, then any transversal that intersects them will create congruent alternate interior angles.
Methods of Proof in Geometry: Geometry Chapter 2 Reasoning And Proof Answer Key

Direct Proof
A direct proof involves proving a statement by showing that it is logically equivalent to a known true statement.
Example: To prove that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees, we can use the fact that the sum of the angles in a quadrilateral is 360 degrees.
Indirect Proof
An indirect proof involves assuming the opposite of the statement to be proven and then showing that this leads to a contradiction.
Example: To prove that the square root of 2 is irrational, we can assume that it is rational and then show that this leads to a contradiction.
Proof by Contradiction
A proof by contradiction is a type of indirect proof that involves assuming the opposite of the statement to be proven and then showing that this leads to a logical contradiction.
Example: To prove that the Pythagorean theorem is true, we can assume that it is false and then show that this leads to a logical contradiction.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of reasoning and proof in geometry?
Reasoning and proof are the foundation of geometry, enabling us to establish the validity of geometric statements and construct a coherent understanding of geometric relationships.
How do I approach solving geometry problems involving reasoning and proof?
Start by identifying the given information and what you need to prove. Apply appropriate reasoning techniques and methods of proof to construct a logical argument that leads to the desired conclusion.
What are some common types of reasoning used in geometry?
Deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, and geometric reasoning are commonly employed in geometry to draw conclusions from given premises.
How can I improve my skills in geometric reasoning and proof?
Practice regularly, engage in problem-solving challenges, and seek guidance from textbooks, online resources, and knowledgeable individuals.