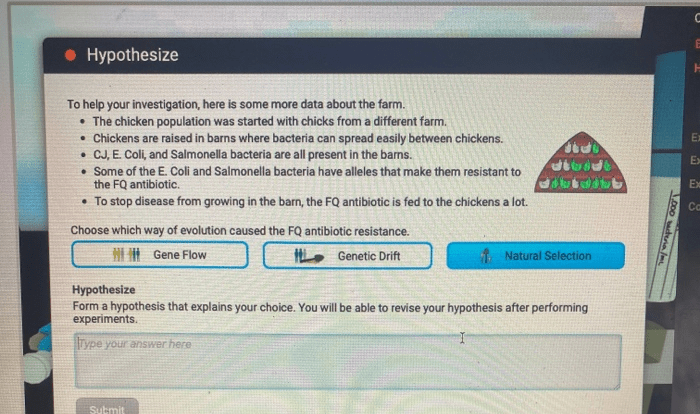
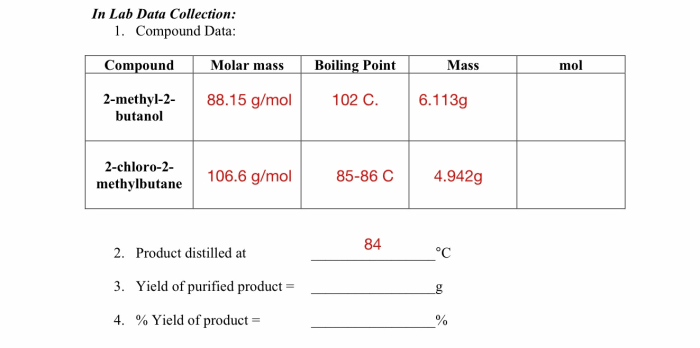
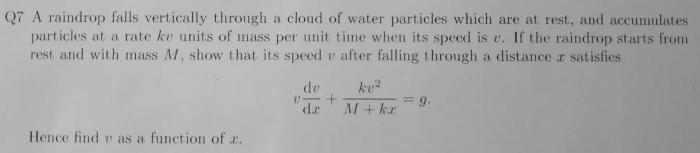Embark on an enlightening journey with the Introduction to Gas Laws Webquest Answer Key, a comprehensive guide that unlocks the secrets of gas behavior. This key provides a profound understanding of the fundamental principles governing gases, empowering you to navigate the complexities of this fascinating realm.
Delve into the historical evolution of gas laws, tracing the footsteps of renowned scientists and their groundbreaking experiments. Discover the intricacies of Boyle’s, Charles’s, Gay-Lussac’s, and the Combined Gas Law, unraveling their mathematical formulas and practical applications.
Introduction to Gas Laws
Gas laws are fundamental principles that describe the behavior of gases under various conditions. They provide a quantitative understanding of the relationship between pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles of a gas. These laws are essential for comprehending the behavior of gases in different systems and applications.
Boyle’s Law, Introduction to gas laws webquest answer key
Boyle’s law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume at constant temperature. Mathematically, it can be expressed as P 1V 1= P 2V 2, where P 1and V 1represent the initial pressure and volume, and P 2and V 2represent the final pressure and volume, respectively.
Boyle’s law has numerous applications, including determining the volume of a gas at different pressures, designing pressure vessels, and understanding the behavior of gases in diving equipment.
Assumptions and limitations:
- Temperature remains constant.
- Gas behaves ideally.
- No chemical reactions occur.
Charles’s Law
Charles’s law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at constant pressure. Mathematically, it can be expressed as V 1/T 1= V 2/T 2, where V 1and T 1represent the initial volume and temperature, and V 2and T 2represent the final volume and temperature, respectively.
Charles’s law has applications in fields such as hot air ballooning, weather forecasting, and the design of temperature-controlled systems.
Assumptions and limitations:
- Pressure remains constant.
- Gas behaves ideally.
- No chemical reactions occur.
Gay-Lussac’s Law
Gay-Lussac’s law states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at constant volume. Mathematically, it can be expressed as P 1/T 1= P 2/T 2, where P 1and T 1represent the initial pressure and temperature, and P 2and T 2represent the final pressure and temperature, respectively.
Gay-Lussac’s law finds applications in the design of pressure gauges, understanding the behavior of gases in combustion engines, and determining the temperature of gases.
Assumptions and limitations:
- Volume remains constant.
- Gas behaves ideally.
- No chemical reactions occur.
Combined Gas Law
The combined gas law combines Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, and Gay-Lussac’s law into a single equation that relates pressure, volume, and temperature changes of a gas. Mathematically, it can be expressed as P 1V 1/T 1= P 2V 2/T 2, where P 1, V 1, and T 1represent the initial conditions, and P 2, V 2, and T 2represent the final conditions.
The combined gas law is widely used in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering, to predict the behavior of gases under different conditions.
Assumptions and limitations:
- Gas behaves ideally.
- No chemical reactions occur.
Query Resolution: Introduction To Gas Laws Webquest Answer Key
What is the significance of gas laws?
Gas laws provide a fundamental framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of gases under varying conditions, enabling scientists and engineers to design and optimize systems involving gases.
How can I use the Introduction to Gas Laws Webquest Answer Key?
This key is designed to complement your learning journey, offering detailed explanations, solved examples, and practice questions to reinforce your understanding of gas laws and their applications.
What are the limitations of gas laws?
Gas laws are based on certain assumptions, such as ideal gas behavior and negligible intermolecular forces. In certain extreme conditions or for non-ideal gases, deviations from these laws may occur.